图+源码,读懂View的Measure方法
持续创作,加速成长!这是我参与「掘金日新计划 · 10 月更文挑战」的第14天,点击查看活动详情
读懂 View 三大绘制方法的文章
图+源码,读懂View的MeasureSpec - 掘金 (juejin.cn)
图+源码,读懂View的Measure方法 - 掘金 (juejin.cn)
前置知识
- 有Android开发基础
- 了解 View 体系
- 了解 View 的
MeasureSpec方法
前言
本篇是 读懂View 系列的第二篇文章,本文将给大家正式开始讲解View绘制的三大方法,本篇将讲述第一个方法—— Measure 方法。
Measure方法有何作用
讲到Measure方法的作用,我们需要回顾一下在View体系(下)一文中学到的页面绘制流程一图,为方便你查看,我把这个绘制流程图搬来这里。
通过此图,我们可以看到,在执行 performTraversals() 方法的时候,其方法内部会依次执行 performMeasure()、performLayout() 和 performDraw() 方法。下面 performTraversals() 的源码是经过的裁剪的,我们可以很清楚的看到三者的执行顺序。
private void performTraversals() {
...
if (!mStopped || mReportNextDraw) {
...
performMeasure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);
...
}
if (didLayout) {
performLayout(lp, mWidth, mHeight);
...
if (!performDraw() && mSyncBufferCallback != null) {
mSyncBufferCallback.onBufferReady(null);
}
...
}
}在上一篇文章中我们提到,在 performMeasure 方法内部,它是会执行 measure() 方法的。所以说,measure() 方法是三大绘制方法中首个执行的方法,其作用是测量 View 的宽和高。它的作用流程又两个,一个是 View 的作用流程,一个是 ViewGroup 的作用流程。两个流程有所不同,下面我们细细道来。
View 的 measure 流程
源码分析
首先我们打开View的源码,找到 onMeasure() 方法,下面代码中,由于注释占据的篇幅较大,我删去了一些。注释中主要说的是,该段代码是用于测量View的宽度和高度,该方法会被 measure() 方法调用,如果继承View使用该方法的话,建议重写以提供更加准确的功能。并且写了一些重写的要求和哪种情况必须重写。
在 onMeasure() 方法中,我们可以看到传入的参数正是上一篇文章中我们讲的 MeasureSpec ,它的参数由 measure() 方法调用的时候传入,而 measure() 方法则是提供给 performMeasure 方法调用来测量的。
/**
* ...省略一大段注释,有兴趣的同学可查阅源码的注释
* @see #getMeasuredWidth()
* @see #getMeasuredHeight()
* @see #setMeasuredDimension(int, int)
* @see #getSuggestedMinimumHeight()
* @see #getSuggestedMinimumWidth()
* @see android.view.View.MeasureSpec#getMode(int)
* @see android.view.View.MeasureSpec#getSize(int)
*/
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
setMeasuredDimension(getDefaultSize(getSuggestedMinimumWidth(), widthMeasureSpec),
getDefaultSize(getSuggestedMinimumHeight(), heightMeasureSpec));
}
public final void measure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
...
if (forceLayout || needsLayout) {
...
if (cacheIndex < 0 || sIgnoreMeasureCache) {
// measure ourselves, this should set the measured dimension flag back
onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);//调用onMeasure()
mPrivateFlags3 &= ~PFLAG3_MEASURE_NEEDED_BEFORE_LAYOUT;
} ...
}
...
}我们发现,onMeasure() 里面只有一个 setMeasuredDimension() 方法。我们接着看一下其代码,它需要传入两个参数,分别是测量的宽度和高度,看一下代码的执行过程,我们可以发现,这段代码是用来设置 View 的宽以及高的。
protected final void setMeasuredDimension(int measuredWidth, int measuredHeight) {
boolean optical = isLayoutModeOptical(this);
if (optical != isLayoutModeOptical(mParent)) {
Insets insets = getOpticalInsets();
int opticalWidth = insets.left + insets.right;
int opticalHeight = insets.top + insets.bottom;
measuredWidth += optical ? opticalWidth : -opticalWidth;
measuredHeight += optical ? opticalHeight : -opticalHeight;
}
setMeasuredDimensionRaw(measuredWidth, measuredHeight);
}
private void setMeasuredDimensionRaw(int measuredWidth, int measuredHeight) {
mMeasuredWidth = measuredWidth;
mMeasuredHeight = measuredHeight;
mPrivateFlags |= PFLAG_MEASURED_DIMENSION_SET;
}我们看到这里,会发现,我们仍未看到 View 的宽以及高在何处进行测量的。
继续点开 getDefaultSize() 的代码,我们在此处可以看到代码中传入了 View 的大小(size),View 的 measureSpec 数据。然后代码执行了以下的步骤。
- 在注释1和2处,通过
MeasureSpec类,获得了specMode和specSize两个数据 - 然后在注释3处,根据不同的模式,放回不同的size大小值
但是在 AT_MOST 和 EXACTLY (就是wrap_content和match_parent)两种模式下,其返回值是一样的,这明显是不对的。所以说,当我们自定义 View 需要 wrap_content 属性时,需要重写 onMeasure() 方法,对该属性进行处理,否则使用 wrap_content 就相当于使用 match_parent。
/**
* Utility to return a default size. Uses the supplied size if the
* MeasureSpec imposed no constraints. Will get larger if allowed
* by the MeasureSpec.
*
* @param size Default size for this view
* @param measureSpec Constraints imposed by the parent
* @return The size this view should be.
*/
public static int getDefaultSize(int size, int measureSpec) {
int result = size;
int specMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(measureSpec);//1
int specSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(measureSpec);//2
switch (specMode) {//3
case MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED:
result = size;
break;
case MeasureSpec.AT_MOST:
case MeasureSpec.EXACTLY:
result = specSize;
break;
}
return result;
}上面 getDefaultSize() 的代码中,在 UNSPECIFIED 模式下,是直接返回传入的 size ,而这个 size 则是由 getSuggestedMinimumWidth() 或者是 getSuggestedMinimumHeight() 方法传递得出,两个方法的处理逻辑是一样的,我们分析其中一个就可。
查阅 getSuggestedMinimumWidth() 的代码,我们会发现,它的逻辑是:当无背景时,直接返回 mMinWidth ;而当有背景的时候,返回的是 mMinWidth 和 背景(Drawable)最小宽度两者之间的最大值。
/**
* Returns the suggested minimum width that the view should use. This
* returns the maximum of the view's minimum width
* and the background's minimum width
* ({@link android.graphics.drawable.Drawable#getMinimumWidth()}).
* <p>
* When being used in {@link #onMeasure(int, int)}, the caller should still
* ensure the returned width is within the requirements of the parent.
*
* @return The suggested minimum width of the view.
*/
protected int getSuggestedMinimumWidth() {
return (mBackground == null) ? mMinWidth : max(mMinWidth, mBackground.getMinimumWidth());
}
//getSuggestedMinimumHeight()同理上述代码中的 mMinWidth ,是可以通过 Android:minWidth 这个属性设置,或者是通过 View 的 setMinimumWidth()这个方法来设置值,若不设置,则为默认值0 。下面给出其get和set代码供大家查看。
/**
* Returns the minimum height of the view.
*
* @return the minimum height the view will try to be, in pixels
*
* @see #setMinimumHeight(int)
*
* @attr ref android.R.styleable#View_minHeight
*/
@InspectableProperty(name = "minHeight")
public int getMinimumHeight() {
return mMinHeight;
}
/**
* Sets the minimum height of the view. It is not guaranteed the view will
* be able to achieve this minimum height (for example, if its parent layout
* constrains it with less available height).
*
* @param minHeight The minimum height the view will try to be, in pixels
*
* @see #getMinimumHeight()
*
* @attr ref android.R.styleable#View_minHeight
*/
@RemotableViewMethod
public void setMinimumHeight(int minHeight) {
mMinHeight = minHeight;
requestLayout();
}
//对应的Width方法同理接着,我们看一下 mBackground.getMinimumWidth() 这个背景宽度的获取代码,由于这个背景类是 Drawable 类型的,所以这个方法也是在 Drawable 类下面的。我们看到方法中对 intrinsicWidth 进行判断,而当他未被设置固有宽度的时候 intrinsicWidth 则为-1,那么返回的值将为0 。反之,则返回固有的宽度。
/**
* Returns the minimum width suggested by this Drawable. If a View uses this
* Drawable as a background, it is suggested that the View use at least this
* value for its width. (There will be some scenarios where this will not be
* possible.) This value should INCLUDE any padding.
*
* @return The minimum width suggested by this Drawable. If this Drawable
* doesn't have a suggested minimum width, 0 is returned.
*/
public int getMinimumWidth() {
final int intrinsicWidth = getIntrinsicWidth();
return intrinsicWidth > 0 ? intrinsicWidth : 0;
}
/**
* Returns the drawable's intrinsic width.
* <p>
* Intrinsic width is the width at which the drawable would like to be laid
* out, including any inherent padding. If the drawable has no intrinsic
* width, such as a solid color, this method returns -1.
*
* @return the intrinsic width, or -1 if no intrinsic width
*/
public int getIntrinsicWidth() {
return -1;
}View的Measure流程图
根据上面的源码分析,得出该过程的图为
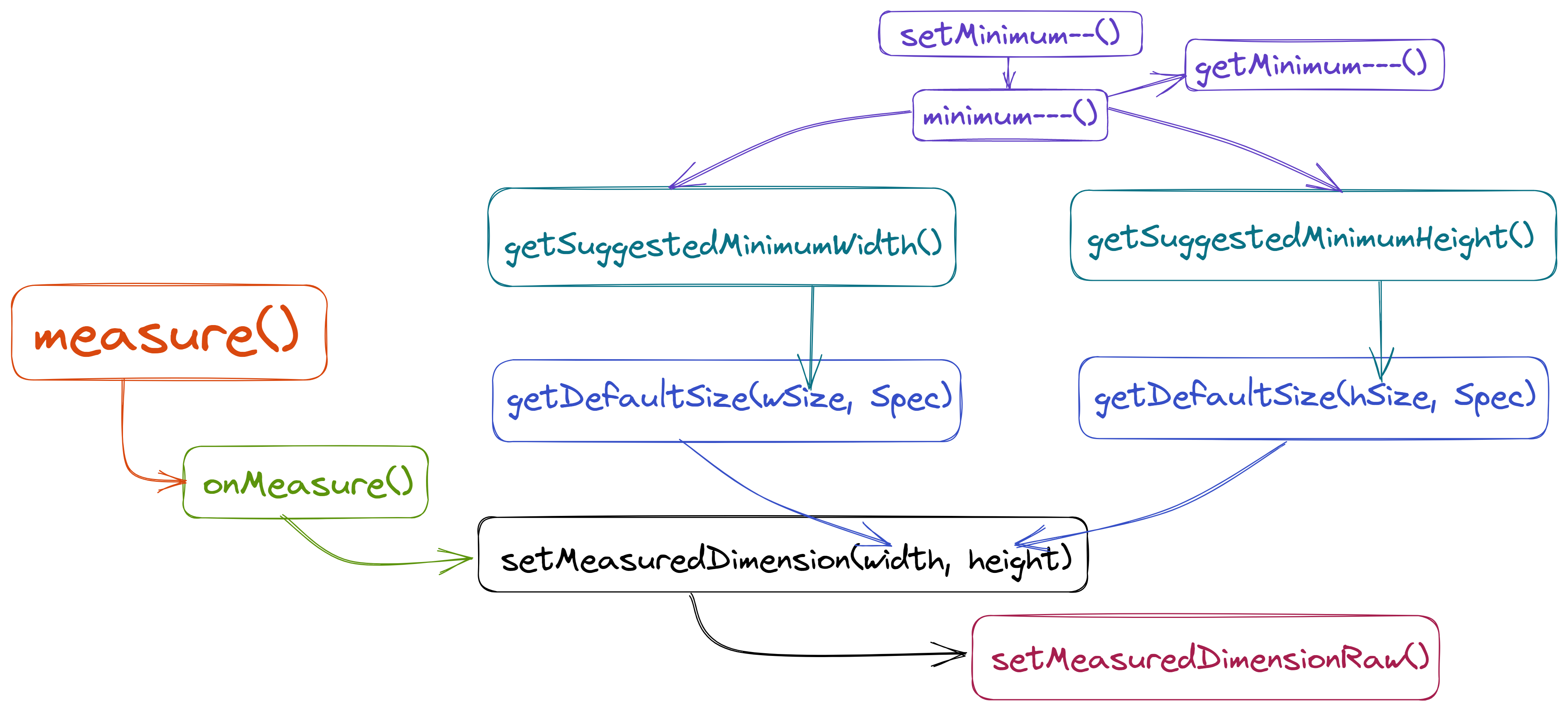
ViewGroup 的 measure 流程
源码分析
对于 ViewGroup 的 measure 流程,与 View 不同的地方就是:它不仅要测量自身,还要遍历的调用子元素的measure方法。
我们知道,ViewGroup 是继承自 View 的,所以,它可以使用 View(实际上让子类重写实现) 的 measure() 和 onMeasure() 方法。我们直接查看它实现遍历子类的方法即可。
其遍历子类的方法是 measureChildren() 。阅读其代码可发现,它遍历每一个子元素,调用的是 measureChild() 方法。而 measureChild() 方法内部,是获取到子元素(自身)的 LayoutParams (注释1)和父布局的 parentWidthMeasureSpec() (注释2)一同传入到 getChildMeasureSpec() 中,从而得出子布局的 MeasureSpec 信息。这和上一篇文章中,根布局(DecorView)获取 MeasureSpec 的条件是不同的。由此我们可知,除根布局外,其他View的 MeasureSpec 都与自身的 LayoutParams 和父布局的 MeasureSpec 有关。
/**
* Ask all of the children of this view to measure themselves, taking into
* account both the MeasureSpec requirements for this view and its padding.
* We skip children that are in the GONE state The heavy lifting is done in
* getChildMeasureSpec.
*
* @param widthMeasureSpec The width requirements for this view
* @param heightMeasureSpec The height requirements for this view
*/
protected void measureChildren(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
final int size = mChildrenCount;
final View[] children = mChildren;
for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i) {
final View child = children[i];
if ((child.mViewFlags & VISIBILITY_MASK) != GONE) {
measureChild(child, widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
}
}
}
/**
* Ask one of the children of this view to measure itself, taking into
* account both the MeasureSpec requirements for this view and its padding.
* The heavy lifting is done in getChildMeasureSpec.
*
* @param child The child to measure
* @param parentWidthMeasureSpec The width requirements for this view
* @param parentHeightMeasureSpec The height requirements for this view
*/
protected void measureChild(View child, int parentWidthMeasureSpec,
int parentHeightMeasureSpec) {
final LayoutParams lp = child.getLayoutParams();//1
final int childWidthMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(parentWidthMeasureSpec,
mPaddingLeft + mPaddingRight, lp.width);//2
final int childHeightMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(parentHeightMeasureSpec,
mPaddingTop + mPaddingBottom, lp.height);
child.measure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);
}接着我们来看一下,这里测量普通View的 getChildMeasureSpec() 方法,是如何执行的。
我们可以看到,其流程和获得 DecorView 的 getRootMeasureSpec() 方法是差不多的。有一个不同且需要注意的地方是下面注释1处,我们发现当父布局的模式为AT_MOST时,子元素无论是 MATCH_PARENT 还是 WRAP_CONTENT ,他们的返回值都是一模一样的。所以,当我们要在使用属性为 WRAP_CONTENT 时,指定默认的宽和高。
/**
* Does the hard part of measureChildren: figuring out the MeasureSpec to
* pass to a particular child. This method figures out the right MeasureSpec
* for one dimension (height or width) of one child view.
*
* The goal is to combine information from our MeasureSpec with the
* LayoutParams of the child to get the best possible results. For example,
* if the this view knows its size (because its MeasureSpec has a mode of
* EXACTLY), and the child has indicated in its LayoutParams that it wants
* to be the same size as the parent, the parent should ask the child to
* layout given an exact size.
*
* @param spec The requirements for this view
* @param padding The padding of this view for the current dimension and
* margins, if applicable
* @param childDimension How big the child wants to be in the current
* dimension
* @return a MeasureSpec integer for the child
*/
public static int getChildMeasureSpec(int spec, int padding, int childDimension) {
int specMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(spec);
int specSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(spec);
int size = Math.max(0, specSize - padding);
int resultSize = 0;
int resultMode = 0;
switch (specMode) {
// Parent has imposed an exact size on us
case MeasureSpec.EXACTLY:
if (childDimension >= 0) {
resultSize = childDimension;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) {
// Child wants to be our size. So be it.
resultSize = size;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT) {
// Child wants to determine its own size. It can't be
// bigger than us.
resultSize = size;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.AT_MOST;
}
break;
// Parent has imposed a maximum size on us
case MeasureSpec.AT_MOST:
if (childDimension >= 0) {
// Child wants a specific size... so be it
resultSize = childDimension;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) {
// Child wants to be our size, but our size is not fixed.
// Constrain child to not be bigger than us.
resultSize = size;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.AT_MOST;
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT) {
// Child wants to determine its own size. It can't be
// bigger than us.
resultSize = size;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.AT_MOST;//1
}
break;
// Parent asked to see how big we want to be
case MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED:
if (childDimension >= 0) {
// Child wants a specific size... let them have it
resultSize = childDimension;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) {
// Child wants to be our size... find out how big it should
// be
resultSize = View.sUseZeroUnspecifiedMeasureSpec ? 0 : size;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED;
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT) {
// Child wants to determine its own size.... find out how
// big it should be
resultSize = View.sUseZeroUnspecifiedMeasureSpec ? 0 : size;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED;
}
break;
}
//noinspection ResourceType
return MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(resultSize, resultMode);
}到此就讲完 ViewGroup 源码的measure了,对其子类实现 onMeasure() 方法的感兴趣的同学,可以查看一下源码
ViewGroup的measure流程图
给出 ViewGroup 的流程图,希望能更好的帮助理解
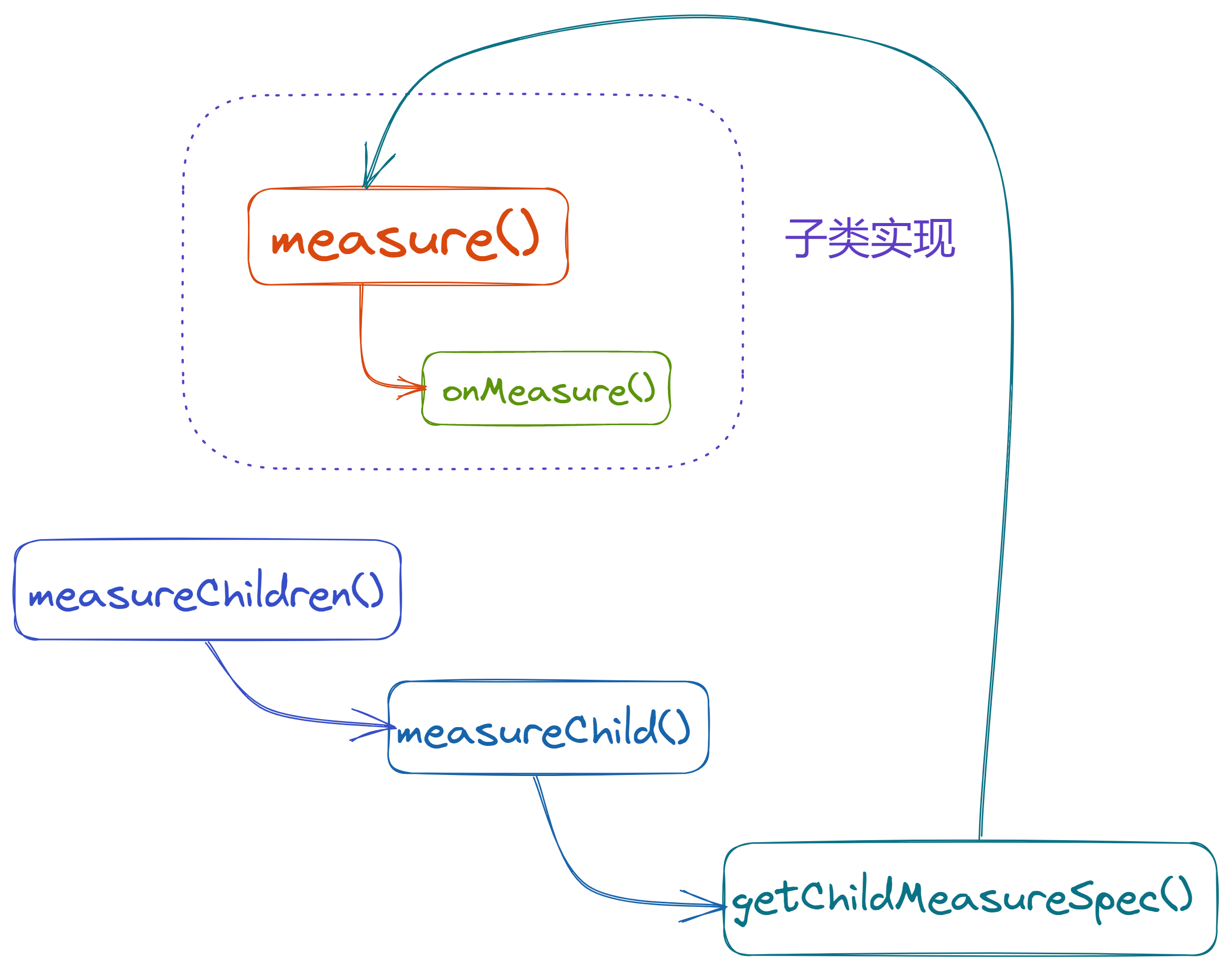
疑问解答
自定义View时,如何设置 wrap_content 类型
前文讲到,在自定义 view 的时候,我们需要将重写 onMeasure() 方法,对 wrap_content 属性进行处理,否则使用 wrap_content 就相当于使用 match_parent。那么应该如何对其属性处理呢?
其实很简单,我们只需要对 View 指定一个默认的内部宽和高,并在判断到是该属性的时候设置此宽和高即可。对于其他属性,则使用内部测量的值即可。具体参考代码如下:
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
int widthSpecMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec);
int widthSpecSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec);
int heightSpecMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec);
int heightSpecSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec);
//宽和高都是 wrap_content 的时候,指定默认的宽高值即可。默认值是啥,自由衡量
if (widthSpecMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST
&& heightSpecMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST) {
setMeasuredDimension(200, 200);
} else if (widthSpecMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST) {
setMeasuredDimension(200, heightSpecSize);
} else if (heightSpecMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST) {
setMeasuredDimension(widthSpecSize, 200);
}
}如何获取到真实宽高(measure 结果)
如何获取到真实 measure 值?这个问题怎么来的呢?难道还有假的值吗?
一般来说,使用 getMeasuredWidth() 就可以获取到对应的 Measure 值了,但是获取的时机不同的时候,可能会导致获取到的值是错误的,因为有的是需要多轮 Measure 才能得出最后的值的。所以要获取到最稳妥的 measure 值的话,是需要在 onLayout 中获取的。
如何在 Activity 启动后就获取 measure 值
这个问题如果我们关注的是启动后就获取,那么就会得出答案是在 onCreate() 或者 onResume() 中获取。但是有一点我们不应该忽略的,那就是 measure 过程与 Activity 的生命周期过程并不是同步进行的。那么怎么办呢?实际上我们应该使用 View 中的一些特性方法,借助他们在 measure 流程结束的时候来获取到对应的值。
Activity/View#onWindowFocusChanged
onWindowFocusChanged 方法是在 View 初始化结束之后执行的,那么自然 measure 流程也已经结束了,所以该方法下获取到的可以是正确测量后的值。但是要注意,这个方法会在聚焦和失焦后被调用,容易出现多次调用的情况。
@Override public void onWindowFocusChanged(boolean hasFocus) { super.onWindowFocusChanged(hasFocus); if (hasFocus) { int width = view.getMeasuredWidth(); int height = view.getMeasuredHeight(); Log.d(TAG, "onWindowFocusChanged, width= " + view.getMeasuredWidth() + " height= " + view.getMeasuredHeight()); } }view.post(runnable)
view.post 使用了 Handler,将消息投递到消息队列的尾部,当 Looper 调用执行的时候,View 已经初始化好了。
那么为什么调用的时候就初始化好了呢?
通过 View.post() 添加的任务,是在 View 绘制流程的开始阶段,将所有任务重新发送到消息队列的尾部,此时相关任务的执行已经在 View 绘制任务之后,即 View 绘制流程已经结束,此时便可以正确获取到 View 的宽高了。
具体代码如下:
@Override protected void onStart() { super.onStart(); view.post(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { int width = view.getMeasuredWidth(); int height = view.getMeasuredHeight(); } }); }ViewTreeObserver
使用 ViewTreeObserver 的众多接口都可以实现该功能,比如 OnGlobalLayoutListener() 接口,但是要注意 View 树可见性改变的时候,OnGlobalLayoutListener() 就会被回调,所以会出现多次被回调的可能。
@Override protected void onStart() { super.onStart(); ViewTreeObserver observer = view.getViewTreeObserver(); observer.addOnGlobalLayoutListener(new OnGlobalLayoutListener() { @SuppressWarnings("deprecation") @Override public void onGlobalLayout() { view.getViewTreeObserver().removeGlobalOnLayoutListener(this); int width = view.getMeasuredWidth(); int height = view.getMeasuredHeight(); } }); }
参考
View.java - Android Code Search
Drawable.java - Android Code Search
LinearLayout.java - Android Code Search
《Android进阶之光》

